

investigated the simultaneous scheduling of machines and AGVs in an FMS environment. proposed an intelligent logistics scheduling model and response method with Automated-Guided Vehicles (AGVs) based on the mode of “request-scheduling-response.” Umar et al. For example, aiming at the logistics dynamic scheduling problem in an intelligent manufacturing workshop (IMW), Xu et al. In recent years, many mathematical models and algorithms have been developed for the AGVs task scheduling problem in the manufacturing environment. Functionally similar approaches also include the genetic algorithm and the met heuristics algorithm.
proposed an improved electromagnetism-like mechanism algorithm to minimize both loaded and empty travel distance. Besides, the algorithm has the comparatively strong dependence on the initial status, thereby being prone to fall into the local optimum. solved the UGN design problem by using a tabu search (TS) algorithm but without the consideration of the empty travel distance. However, this algorithm does not take into account the empty travel distance and the result may substantially differ from the actual situation. For example, Ko and Egbelu proposed a multistage design method that determines the direction of the path sequentially, according to the traffic flow, with the objective of minimizing the travel distance of loaded vehicles. To decrease the design time, some heuristic algorithms have been developed. Since the time complexity of the algorithm increases exponentially with the scale of the network, the method is only suitable for small-scale design problems. proposed a branch and bound method to minimize the travel distance of loaded vehicles, which can obtain the optimal solution more stably. For example, aiming at the UGN design problem, Kaspi et al. Many design models and algorithms for these two problems have been proposed in the literature. The unidirectional guide-path network (UGN) design and the AGVS task scheduling are the two main issues that should be addressed when the AGVS is adopted. IntroductionĪs a flexible and high-efficiency logistics system, an automatic-guided vehicle system (AGVS) has broad application prospects in fields such as port transportation, warehousing and distribution, and manufacturing.
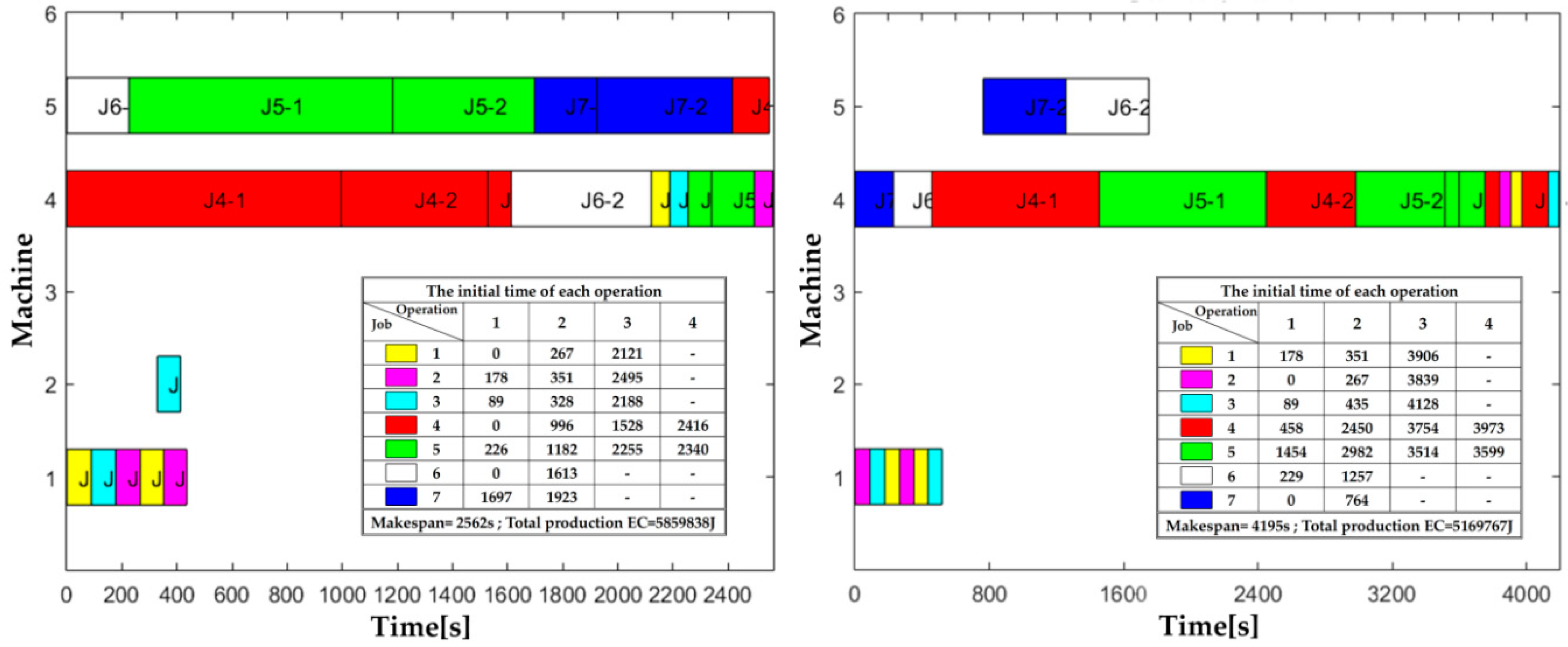
The experimental results show that the integrated design model can formulate the problem more accurately, and the CEGA algorithm is computationally efficient with high solution quality. The neighbourhood search operation, the niche technique, and the elitism strategy are combined to improve the convergence speed and maintain the population diversity. The solutions of the integrated model, i.e., the potential strongly connected UGN and the feasible processing and handling sequence, are, respectively, coded as two different subpopulations with independent and concurrent evolution processes. Secondly, a dual-population collaborative evolutionary genetic algorithm (CEGA) is developed to solve the problems of designing and scheduling in a parallel way. Firstly, an integrated design model of designing UGN and scheduling AGVs simultaneously is proposed, with the objective of minimizing the makespan (i.e., the maximum completion time of all handling tasks), in the consideration of the practical constraints, e.g., the job handling and processing sequence constraints and the AGV number constraint. The motivation of the paper is to bring the coupling factors into the integrated design and solution process. To reduce the complexity, most pertinent literatures only handle these problems one by one, based on the stepwise design methods, thereby neglecting the constraint conditions and the optimization objectives caused by the FMS environment. However, one main challenge lies in the coupling process of the design problem of the unidirectional guide-path network (UGN) and the task scheduling problem of AGVs. In the current industrial fields, automatic guided vehicles (AGVs) are widely employed to constitute the flexible manufacturing system (FMS), owing to their great advantages of routing flexibility and high efficiency.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
